How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting safety regulations, and developing a keen sense of spatial awareness. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently take to the skies, ensuring both safe and successful flights.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding flying experience.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will provide a solid foundation for your drone piloting journey. Get ready for takeoff!
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the drone and the surrounding environment. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and potential legal issues. This section details a comprehensive checklist and safe flight procedures.
Pre-flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight checks minimize risks by identifying potential problems before takeoff. A damaged propeller, low battery, or faulty GPS can all lead to disastrous results. A systematic inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition for a safe and successful flight.
Comprehensive Pre-flight Checklist
The following checklist should be completed before every flight:
- Battery Check: Verify battery level and health. Ensure the battery is fully charged and free from any visible damage.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or damage. Replace any damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Verification: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and control issues.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Verify the gimbal is functioning correctly and is properly calibrated.
- Camera Check (if applicable): Ensure the camera is securely mounted and functioning as expected.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the entire drone for any loose parts or damage.
- Calibration Check: Ensure the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) are properly calibrated.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure
Follow these steps for a safe takeoff and landing:
- Takeoff: Choose a clear, open area away from obstacles. Slowly lift the drone into the air using the throttle control. Maintain visual contact at all times.
- Flight: Operate the drone smoothly and avoid sudden movements. Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people.
- Landing: Slowly descend the drone using the throttle control. Choose a clear landing area and bring the drone down gently.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
| Hazard | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Low Battery | Always monitor battery level and land before it gets critically low. Carry spare batteries. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Fly in areas with good GPS reception. Be prepared to switch to manual control if necessary. |
| Obstacle Collision | Maintain visual contact with the drone. Use obstacle avoidance features (if available). Fly at a safe altitude. |
| Wind Conditions | Avoid flying in high winds. Check the weather forecast before flying. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. This section covers the various controller types, basic flight controls, calibration procedures, and tips for smooth maneuvers.
Drone Controller Types and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in design and features, but most share common functionalities. Some controllers offer customizable buttons and dials for more precise control, while others integrate with mobile apps for enhanced features and telemetry data. Understanding your specific controller’s layout and features is key.
Basic Flight Controls
The four primary flight controls are:
| Control | Effect |
|---|---|
| Throttle | Controls altitude (up and down) |
| Yaw | Rotates the drone left and right |
| Pitch | Tilts the drone forward and backward |
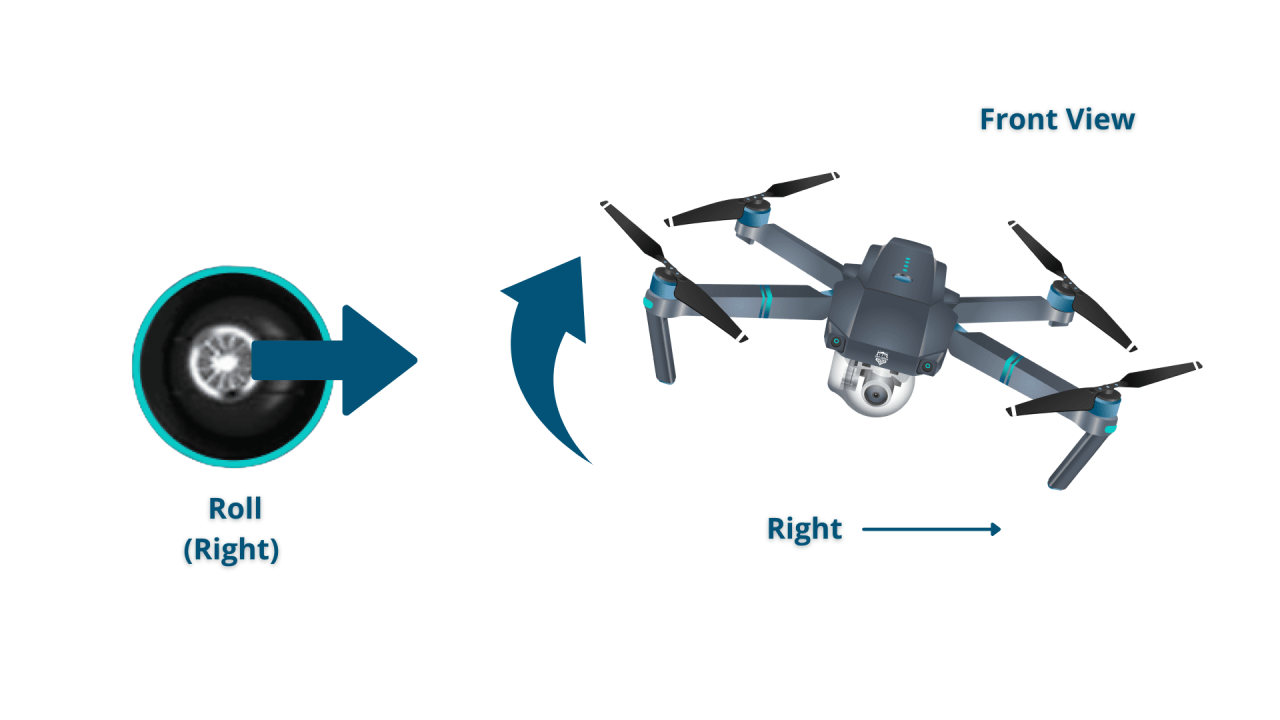
| Roll | Tilts the drone left and right |
Compass and GPS Calibration
Regular calibration ensures accurate flight data. Most drones have automated calibration procedures accessible through the controller or app. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper calibration.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Maneuvers
Practice makes perfect. Start with slow, deliberate movements and gradually increase speed and complexity as you gain experience. Avoid sudden inputs and maintain smooth, consistent control.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including detailed instructions and safety tips, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Proper training ensures responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
Visual Representation of Drone Control Inputs
- Throttle Up: Drone ascends vertically.
- Throttle Down: Drone descends vertically.
- Yaw Left: Drone rotates counter-clockwise.
- Yaw Right: Drone rotates clockwise.
- Pitch Forward: Drone moves forward.
- Pitch Backward: Drone moves backward.
- Roll Left: Drone tilts to the left and moves sideways.
- Roll Right: Drone tilts to the right and moves sideways.
Flight Modes and Autonomous Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes and autonomous features to enhance ease of use and flight capabilities. Understanding these features is crucial for safe and efficient operation.
Flight Mode Comparison
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode unlocks more aggressive maneuvers. GPS mode utilizes satellite positioning for more stable flight.
Autonomous Features: RTH and Waypoint Navigation
Return-to-Home (RTH) automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point, useful in case of signal loss or low battery. Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path, enabling automated aerial photography or inspections.
Setting Up and Using Waypoints
Most drone apps provide tools to create waypoints. You typically define points on a map, set altitude and speed parameters, and the drone will autonomously follow the sequence.
Limitations and Risks of Autonomous Flight
While autonomous features offer convenience, they are not without limitations. GPS accuracy can be affected by environmental factors, and unexpected obstacles may still require manual intervention. Always maintain awareness and be ready to take manual control if necessary.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
The drone’s camera opens up a world of aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to capturing stunning visuals.
Drone Camera Settings and Adjustments
Common settings include ISO (light sensitivity), shutter speed (exposure duration), and aperture (lens opening). Adjusting these settings affects image brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
Achieving Photographic Effects

Shallow depth of field creates a blurred background, emphasizing the subject. Long exposure captures light trails and creates a dreamy effect. Experiment with different settings to achieve desired effects.
Capturing Stable and High-Quality Aerial Footage
Smooth, stable footage requires careful flight control and potentially the use of a gimbal. Avoid sudden movements and maintain a consistent flight path.
Composing Effective Aerial Shots and Choosing Suitable Locations
Consider the perspective, lighting, and composition when choosing a location and framing a shot. Look for interesting angles and visual elements to enhance your aerial photography.
Best Practices for Stunning Aerial Photography and Videography
- Plan your shots in advance, considering lighting, composition, and potential obstacles.
- Use a gimbal for smoother footage.
- Experiment with different camera settings to achieve desired effects.
- Practice smooth and consistent flight control.
- Edit your footage to enhance its visual appeal.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued functionality.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Clean the drone’s body and propellers after each flight. Lubricate moving parts as needed, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Inspect for any signs of damage or wear.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor problems, and communication errors. These issues often stem from battery issues, environmental factors, or mechanical problems.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Issues
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking various components and settings. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting guidance.
Tips for Extending Drone Battery Lifespan
Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging them. Use a proper charger and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Troubleshooting Flowchart (Example: Drone Not Responding to Controls)

A flowchart would visually represent a step-by-step process of checking the controller, battery, radio connection, and drone power, leading to possible solutions like restarting components or replacing the battery.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations. This section highlights key legal aspects of drone operation.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and restrictions in your area regarding drone operation, airspace limitations, and registration requirements.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on the drone’s size, intended use, and location, obtaining permits or licenses might be necessary. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Airspace Restrictions and Limitations
Certain airspace, such as airports and restricted areas, may prohibit drone flights. Always check for airspace restrictions before flying.
Reporting Drone Accidents or Incidents
Report any accidents or incidents involving your drone to the appropriate authorities. This is crucial for safety and legal compliance.
Key Legal Requirements for Drone Operation, How to operate a drone
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Registration | Register your drone with the relevant authority. |
| Licensing | Obtain necessary licenses or permits. |
| Airspace Awareness | Check for airspace restrictions before each flight. |
| Safety Guidelines | Adhere to all safety guidelines and regulations. |
Advanced Drone Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Once you’ve mastered basic operation, explore advanced maneuvers and techniques to elevate your aerial photography and videography.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and 360-degree rotations require practice and skill. Start slowly and gradually increase complexity as your confidence and skill improve.
Specialized Drone Accessories
Gimbal stabilizers ensure smooth footage, while ND filters reduce light for better exposure in bright conditions. These accessories enhance image quality and expand creative possibilities.
Performing Complex Aerial Shots
Drone tracking involves following a moving subject, while orbiting creates circular shots around a point of interest. These techniques require precise control and planning.
Flying in Challenging Conditions
Flying in wind or rain requires additional caution and skill. Adjust flight parameters accordingly and be prepared for unexpected situations.
Visual Examples of Advanced Flight Techniques
- Drone Tracking: A smooth, steady shot following a runner along a trail, showcasing the subject’s movement against a dynamic background.
- Orbiting: A circular shot around a historic building, showcasing its architecture and surrounding landscape from a unique perspective.
- 360-degree Rotation: A fast, controlled rotation revealing a panoramic view of a scenic location.
- Flips and Rolls: Dynamic, controlled aerial maneuvers showcasing the drone’s agility and precision (requires practice and appropriate safety precautions).
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skill, and responsible awareness. From meticulous pre-flight preparations to mastering the nuances of flight controls and camera operation, we’ve explored the key aspects of safe and effective drone piloting. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. So, take to the skies responsibly, capture stunning visuals, and enjoy the exciting world of drone technology!
FAQs
What is the maximum flight time for a typical drone battery?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model and battery size. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, though larger drones with bigger batteries can fly longer.
How do I know if my drone’s GPS signal is strong enough?
Most drones will display the GPS signal strength on their controller screen. Look for a solid indicator or a high percentage. A weak signal may result in inaccurate positioning and potential flight issues.
What should I do if my drone loses its GPS signal mid-flight?
If your drone loses GPS, it will likely enter a failsafe mode. Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function that will attempt to bring it back to its starting point. If this fails, carefully bring the drone down manually, keeping it within visual range.
Can I fly my drone in any location?
No. Drone flight is subject to various regulations and restrictions. Always check local airspace rules and regulations before flying, and be mindful of no-fly zones near airports and other sensitive areas.
